WEBBUTVECKLING 1
History of internet
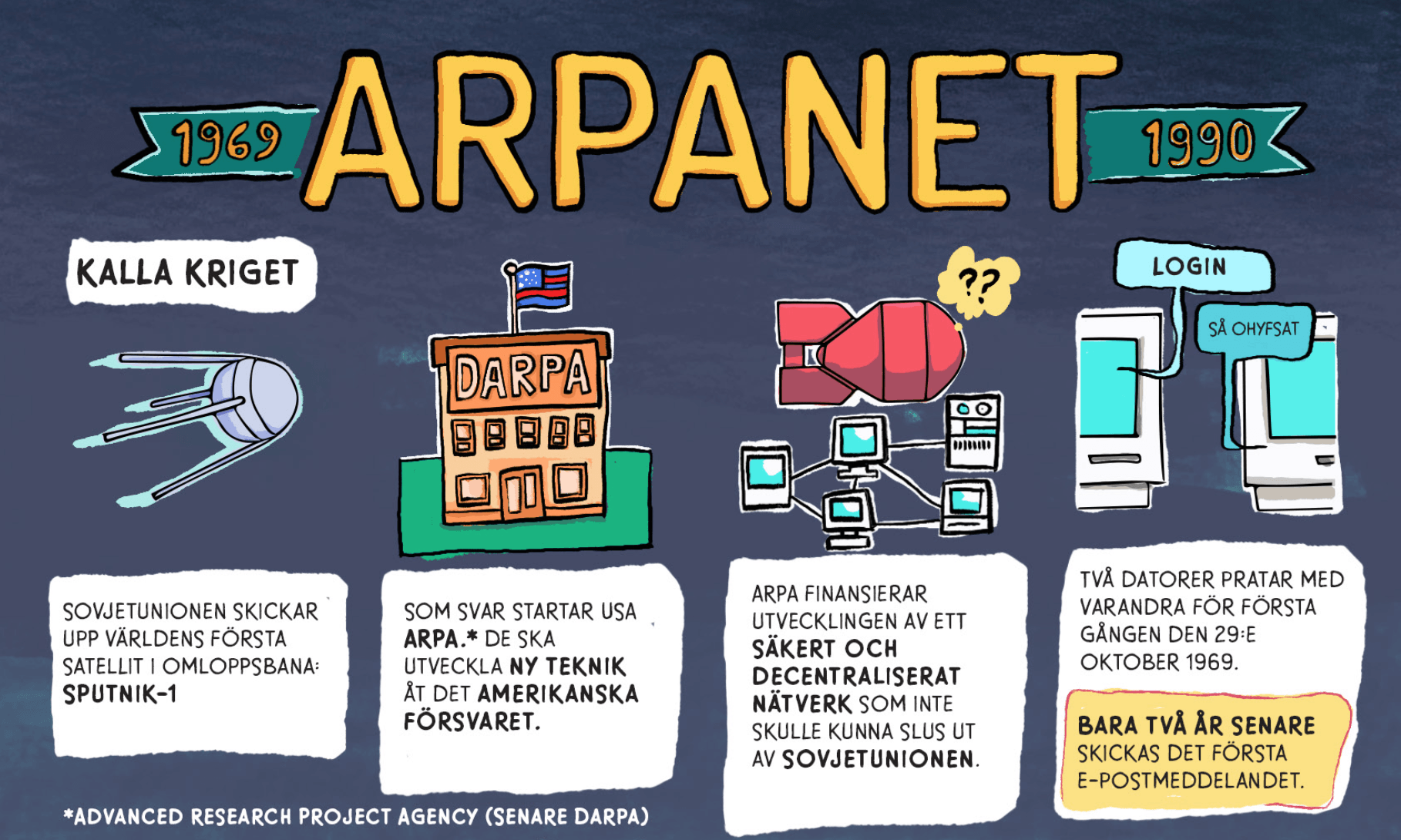
ARPANET is a computer network, began the world's first Internet. It's main task was to switch between projects of the US Department of Defense. The creation of this network was the launch of an artificial Earth satellite in the USSR in 1957. After this event, in order to increase information security in case of war, the United States Department of Defense decided to develop a system for data transmission. The computer network was created by a special agency APRA (Advanced Research Projects Agency), which was responsible for the introduction of new technologies in the United States.
On October 29 1969, a group of researchers managed to get a UCLA computer to interact with a computer at another research institute.
In July 1976, a team of researchers demonstrated for the first time the transmission of data using the TCP protocol over three different networks. The package went along the following route: San Francisco - London - University of Southern California. By the end of its journey, the packet had covered 150,000 km without losing a single bit of information.
In the 1980s, the domain name system emerged and the international adoption of TCP / IP was the beginning of the Internet.
In the 1990s, individuals began to use the Internet more heavily as commercial operators offered connections to home users.
In the 2000s, with the advent of mobile devices and social networks, the Internet became widespread.
On October 29 1969, a group of researchers managed to get a UCLA computer to interact with a computer at another research institute.
In July 1976, a team of researchers demonstrated for the first time the transmission of data using the TCP protocol over three different networks. The package went along the following route: San Francisco - London - University of Southern California. By the end of its journey, the packet had covered 150,000 km without losing a single bit of information.
In the 1980s, the domain name system emerged and the international adoption of TCP / IP was the beginning of the Internet.
In the 1990s, individuals began to use the Internet more heavily as commercial operators offered connections to home users.
In the 2000s, with the advent of mobile devices and social networks, the Internet became widespread.